Do You Have A Project We Can Help With?
Heat treatment services
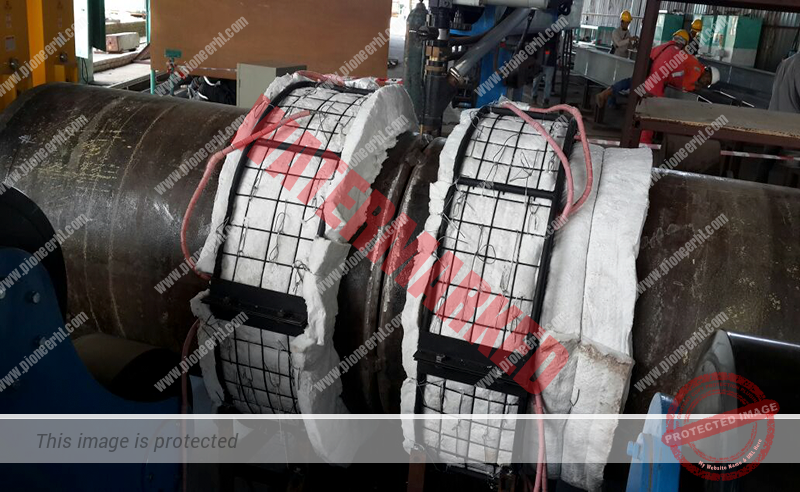
We provide heat treatment services which are typically carried out during fabrication and/or installation of piping systems, where welding activities will cause a rise in material temperatures which could potentially affect the mechanical properties of the components involved. Heat treatment is a material treatment process where critical thermal processes are applied to maintain the structural integrity (e.g. increased ductile quality, increased resistance to heat and vibrations, reduced brittleness which results from the rapid heating and cooling of the welding process), performance, and longevity of welded joints (i.e. strengthened joints).
We offer 2 types of heat treatment services, namely pre-heating and post-weld heat treatment:
- Pre-heating service involves raising the temperature of the base metal in the weld area before and during welding. This process reduces thermal shock and the risk of hydrogen-induced cracking, slows the cooling rate after welding which promotes ductile microstructure formation, improves weld penetration and fusion, enhances overall weld quality and reliability, and ultimately reduces the risk of weld defects.
- Post-weld heat treatment service involves a controlled process of reheating the welded area to a specific temperature after welding, then slowly cooling it. This process relieves residual stresses from welding that could lead to distortion or premature failures, restore ductility and toughness at the heat-affected areas, enhances fatigue resistance and overall lifespan of the piping systems and structures, and ensures compliance with applicable codes and customer’s specifications.


Flange management
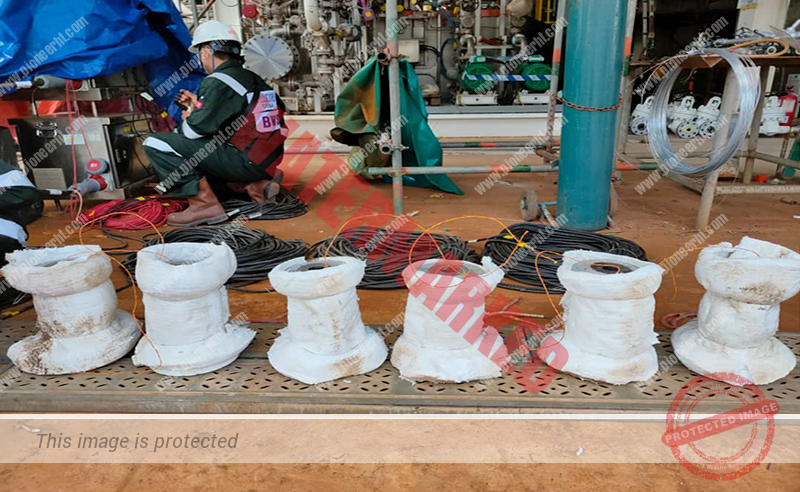
We offer flange management services which aim to provide a secure and leak-tight connection between flanged joints on pipes, rotating equipment and mechanical units, as well as improve structural integrity of the piping systems that operate under high pressure and extreme conditions. Flange management is a form of quality control measure. Timely flange management reduces operational downtime and safety hazards by ensuring compliance with standards, especially in high-risk environments such as refineries, offshore platforms, petrochemical plants and utility plants. Controlled bolting is part of flange management which includes manual torquing, hydraulic bolt torquing and hydraulic bolt tensioning.
For maintenance projects, as part of flange management, we offer the following services:
- Valve servicing which include the removal, reinstatement, overhaul, servicing, testing and painting of valves comprising manual valves, pressure safety valves, isolation valves and pressure relief valves, in which the servicing is carried out in-house. This is to ensure that the valves function properly and safely within the piping system. Servicing of control valves is outsourced to third party subcontractors and includes cleaning, packing gland replacement, seat lapping machining, calibration and hydrostatic testing of control valves. We also replace worn-out packing gland inside the valves to create a tight seal. Finally, we will conduct hydrotesting to verify the integrity of the joints.
- Heat exchanger tube bundle routine inspection and servicing is the regular maintenance of the tube bundle to ensure efficient operations, structural integrity and compliance with safety standards. The process begins with removing the tube bundle from the shell of a heat exchanger using tube bundle extractor machine. The tube bundle will be inspected visually for damage (e.g. cracks, corrosion and fouling) and hydrotesting will be performed to detect internal defects or leaks. Then it will be cleaned using mechanical tools (brushes and scrapers), chemical cleaning agents, or high-pressure hydrojetting to remove fouling and deposits.
Tube bundle servicing includes repairing or plugging damaged tubes, replacing gaskets, re-tubing if necessary, and ensuring proper alignment during reassembly. Finally, all findings and actions are documented for compliance with the required standards and future maintenance planning. All the work required can be done by our in-house team.
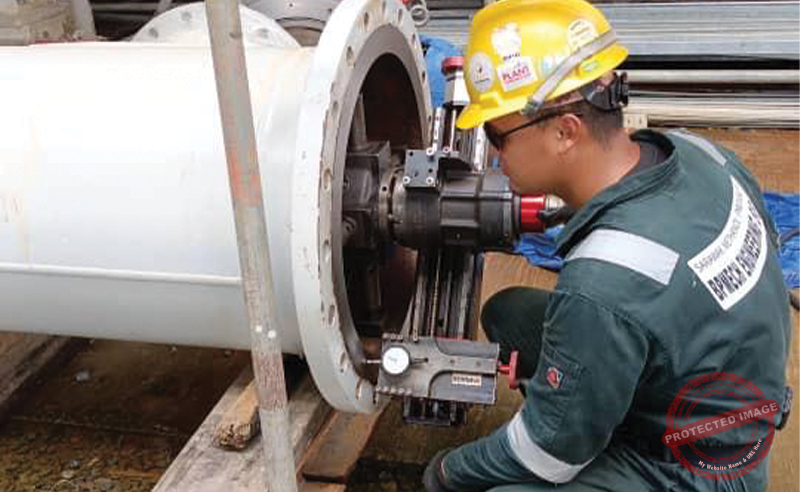

NDT services
NDT refers to a set of techniques used to inspect, evaluate and ensure the integrity of piping systems, piping structures and mechanical units without causing damage to the material or disrupting operations. NDTs are compulsory quality assurance and testing procedures that are carried out after works are completed to ensure the reliability of a welded joint, the properties of the steel materials meet the required specification, and that there are no hidden defects such as cracks, corrosion, inclusions, and dimensional inaccuracies of the piping systems, piping structures and mechanical units. This is because any failure within the piping systems, piping structures or mechanical units can result in catastrophic consequences, including leaks, explosions, environmental contamination, or even loss of life.
We provide NDT services for the piping works that we carry out, as well as for piping works carried out and mechanical units fabricated by other subcontractors. The range of NDT services that we offer are as set out below:
Conventional NDT methods
-
-
Industrial radiograph testing
A method that uses ionizing radiation such as X-rays or gamma rays to inspect the internal structure of a material or component. It is used to detect internal defects such as cracks, porosity, voids or improper weld fusions.
-
Phased array ultrasonic testing
A method that uses multiple ultrasonic elements and electronic time delays to steer and focus sound beams without moving the probe, to detect flaws, measure thickness, and evaluate material properties in welds, metals and composites.
-
Hardness testing
A method of evaluating the hardness of a material without causing significant damage or alteration to the tested material. It measures the resistance of material to deformation in a way that does not adversely affect the material’s performance.
-
Dye penetrant testing
A method that involves applying liquid penetrant (i.e. a coloured or fluorescent dye) to detect surface-breaking defects such as porosity, cracks, seams, laps and cold shuts of open surface of nonporous materials.
-
Magnetic particle testing
A method that involves magnetising ferromagnetic materials such as carbon steel, to detect surface and near-surface flaws such as cracks or voids.
-
Ultrasonic flaw detection
A method that uses high-frequency ultrasonic sound waves to detect defects or imperfections on the surface of materials, or detect internal flaws, discontinuities, and defects within materials.
-
Positive material identification (“PMI”)
A method used to verify and analyse the chemical composition and alloy grade of metallic materials and components. PMI is crucial when there is uncertainty or lack of material certification, ensuring that metals and alloys conform to required standards and specifications for safety, quality and performance.
-
Ultrasonic thickness gauging
A method that uses high-frequency ultrasonic sound waves to measure the thickness of the materials.
-
Ferrite testing
A method used to measure the ferrite content in austenitic and duplex stainless steel materials and welds. Ferrite testing determines the percentage of ferrite phase present in the microstructure of the stainless steels, which directly affects their mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, weldability, and overall durability.
-
Leak testing
A method used to detect, locate and quantify leaks in pressure boundaries, vessels, pipelines, or any sealed system. It ensures the integrity, safety, and performance of critical systems by identifying leaks that could cause failures or inefficiencies.
-
Visual inspection
A method of direct examination of a component or structure using the human eye, sometimes assisted by optical tools, to detect visible surface defects or irregularities such as cracks, corrosion, misalignments, deformations, welding defects and surface discontinuities.
-
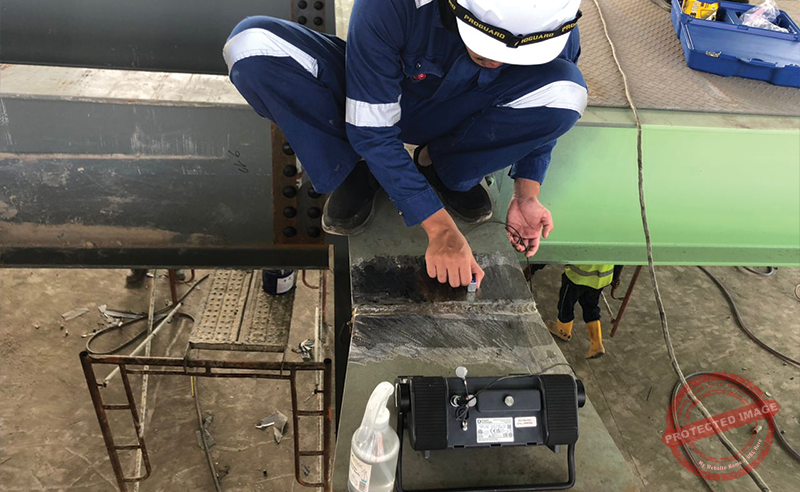
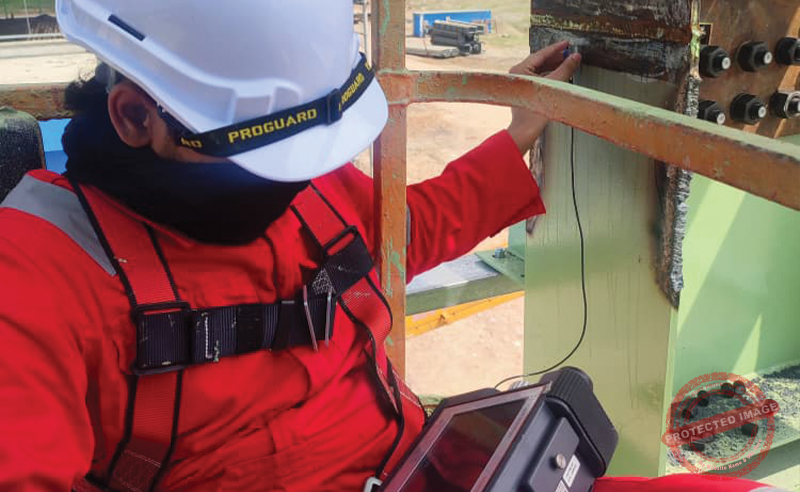
Holiday detector testing
A method of inspecting coated or painted surfaces to find defects such as holes, pinholes, cracks, or voids, that allow electrical current to pass through, indicating breaks or flaws in the non-conductive protective layer. These defects in coatings may compromise the integrity of the coating as they can lead to corrosion and premature failure of the underlying metal.
Advance NDT methods
-
Time of flight diffraction
A method that uses diffracted sound waves that bend around the tips of flaws, for detection and accurate sizing of internal flaws such as cracks and lack of fusion, in welds and other structural materials.
-


Clients We Have Collaborated With
Our provision of excellent services has earned us great credibility and reputation in the heat treatment industry where many companies have approached us for partnerships.














